Navigating Challenges as a Transfemme Individual

The term “transfeminine” encompasses a broad spectrum of identities and expressions. It describes individuals who were assigned male at birth but identify more closely with femininity than masculinity. This identity is a vital part of the broader transgender umbrella, which includes a diverse range of gender identities and expressions. Transfeminine people may or may not choose to medically transition, and their gender expression can vary widely.
Summary
This article defines transfeminine identities and emphasizes the diversity of gender expressions and transition paths, shaped by personal choice and cultural context. It examines the transfeminine flag’s evolution and symbolism, and outlines key challenges such as discrimination, media misrepresentation, safety in public spaces, healthcare barriers, mental health needs, and uneven legal recognition. The piece underscores the role of self-reflection, community support, and overcoming internalized transphobia. It provides concrete allyship actions—education, dialogue, challenging bias, policy advocacy, workplace inclusivity, creating safe spaces, and offering emotional support—to help transfemme individuals thrive.
Exploring Gender Identity and Expression
Transfeminine individuals navigate a complex landscape of gender identity and expression. Some may identify strictly as female, while others embrace non-binary or gender-fluid identities. This diversity underscores the importance of viewing gender as a spectrum rather than a binary concept. Transfeminine people may express their femininity through clothing, makeup, or behavior, and these expressions can be fluid and change over time.
The Role of Medical Transition
Medical transition is a deeply personal choice for transfeminine individuals. While some may pursue hormone therapy or gender-affirming surgeries, others may opt not to, either by choice or due to barriers such as cost or healthcare access. It’s crucial to respect each individual’s decisions regarding their transition journey, understanding that there is no single “right” way to be transfeminine.
The Intersection of Culture and Identity
Cultural backgrounds can significantly influence transfeminine identities. In some cultures, there are historical precedents for third-gender roles, offering a unique context for transfeminine individuals. These cultural narratives can impact how transfeminine people understand and express their identities, highlighting the need for culturally sensitive support and acknowledgment.
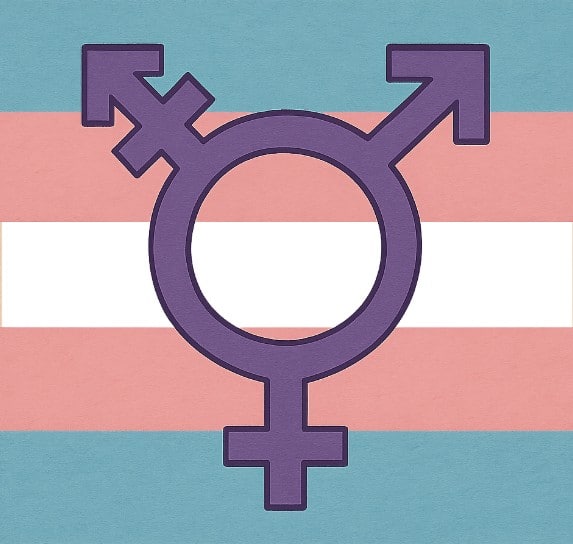
The Transfeminine Flag: A Symbol of Pride

Flags play a crucial role in representing identities and fostering a sense of community. The transfeminine flag, much like other pride flags, serves as a powerful symbol of visibility and solidarity. It features soft hues of pink and blue, often combined with white, symbolizing a blend of traditional gender colors and the fluidity of gender identity.
The Evolution of the Transfeminine Flag
The transfeminine flag has evolved over time to represent the community’s growing diversity and strength. Initially, variations of the transgender flag were used, but the need for a distinct symbol led to the creation of the transfeminine flag. This evolution reflects the community’s resilience and the ongoing journey towards visibility and recognition.
Symbolism and Color Significance
Each color on the transfeminine flag carries its own significance. The pink often represents traditional femininity, while the blue acknowledges the masculine aspects that some transfeminine individuals may relate to. The white stripe is a nod to those who are non-binary or gender non-conforming, emphasizing the inclusivity and diversity within the transfeminine community.
The Flag as a Tool for Advocacy
Beyond its role as a symbol of pride, the transfeminine flag serves as a tool for advocacy. Displaying the flag at events, marches, and in public spaces raises awareness and fosters conversations about transfeminine identities. It is a visual reminder of the ongoing fight for recognition, rights, and equality.
Challenges Faced by the Transfemme Community
The journey of a transfemme individual is often fraught with unique challenges, ranging from societal discrimination to personal struggles with identity and acceptance. Understanding these challenges is crucial in fostering a more inclusive and supportive society.
Societal Discrimination and Misunderstandings
Transfeminine individuals often face significant societal discrimination. Misunderstandings about what it means to be transfeminine can lead to prejudice and marginalization. Many transfemme people encounter difficulties in accessing healthcare, employment opportunities, and safe living environments due to systemic discrimination.
The Impact of Misrepresentation in Media
Media representation plays a significant role in shaping societal perceptions. Transfeminine individuals are frequently misrepresented or underrepresented in media, which contributes to misconceptions and stereotypes. Advocating for accurate and diverse representations can help dismantle harmful narratives and promote a more nuanced understanding of transfeminine identities.
Navigating Public Spaces
Public spaces can often be challenging for transfeminine individuals. Experiences of harassment or discrimination in places such as bathrooms, public transportation, or social venues highlight the need for increased awareness and inclusivity. Creating safer public environments requires both policy changes and shifts in societal attitudes.
Addressing Workplace Discrimination
Workplace discrimination remains a significant barrier for transfeminine individuals. Biases and lack of understanding can lead to unfair hiring practices, unequal opportunities, and hostile work environments. Advocating for inclusive workplace policies and providing diversity training can help create more equitable professional spaces.
Personal Struggles and Identity Acceptance

Personal struggles with identity and acceptance are common among transfeminine individuals. The journey to self-discovery can be complex, involving internal conflicts about gender expression and fears of societal rejection. Accepting oneself and finding a supportive community can be transformative steps in overcoming these challenges.
The Role of Self-Reflection
Self-reflection is a critical aspect of understanding and embracing one’s transfeminine identity. It involves exploring personal feelings and experiences to gain clarity on one’s gender identity. This process can be emotionally challenging but ultimately rewarding, leading to greater self-acceptance and empowerment.
The Importance of Community Support
Community support is invaluable for transfeminine individuals navigating personal struggles. Connecting with others who share similar experiences provides a sense of belonging and validation. Support groups, online communities, and local organizations can offer spaces for sharing stories, advice, and encouragement.
Overcoming Internalized Transphobia
Internalized transphobia can be a significant hurdle for transfeminine individuals. Societal messages that devalue or stigmatize transgender identities can lead to self-doubt and shame. Overcoming this requires unlearning harmful narratives and embracing one’s identity with pride and confidence.
Healthcare Barriers
Access to appropriate healthcare is a significant challenge for the transfemme community. Many healthcare providers lack the training and understanding necessary to provide competent care for transgender individuals. This can lead to inadequate medical support and a lack of access to gender-affirming treatments.
The Need for Trans-Inclusive Medical Training
Improving healthcare for transfeminine individuals starts with education. Medical professionals need comprehensive training on transgender health issues to provide competent and respectful care. Incorporating trans-inclusive curricula in medical schools and ongoing professional development can enhance healthcare experiences for the transfemme community.
Access to Gender-Affirming Treatments
Gender-affirming treatments are crucial for many transfeminine individuals seeking to align their physical appearance with their gender identity. Barriers such as cost, insurance coverage, and limited availability can hinder access to these treatments. Advocacy for policy changes and increased funding is essential to improve access to necessary healthcare services.
Addressing Mental Health Needs
Mental health support is an integral component of healthcare for transfeminine individuals. Experiences of discrimination, identity struggles, and societal pressures can impact mental well-being. Providing access to trans-competent mental health professionals and resources is vital for supporting the overall health of the transfemme community.
Legal and Policy Issues
Legal recognition of transfeminine identities varies widely across different regions and countries. In many places, legal documents do not reflect the gender identity of transfemme individuals, leading to difficulties in accessing services and legal protections. Advocacy for more inclusive policies and legal recognition remains an important focus for the community.
The Importance of Legal Gender Recognition
Legal gender recognition is essential for the dignity and rights of transfeminine individuals. Accurate legal documents, such as IDs and passports, are crucial for accessing services and protections. Advocating for streamlined and accessible processes for legal gender changes can reduce barriers and improve the quality of life for transfemme individuals.
Fighting for Anti-Discrimination Laws
Anti-discrimination laws are vital for protecting the rights of transfeminine individuals in various aspects of life, including employment, housing, and healthcare. Advocacy efforts focus on enacting and enforcing comprehensive anti-discrimination legislation to ensure equal opportunities and protections for the community.
Navigating International Legal Landscapes
Transfeminine individuals face different legal challenges depending on their geographical location. While some countries have progressive laws and protections, others may lack recognition or have punitive policies. Understanding these international disparities is crucial for global advocacy and support efforts.
Supporting Transfemme Individuals
Creating a supportive environment for transfeminine people involves both individual actions and broader societal changes. Allies play a crucial role in advocating for and supporting the transfemme community.
Educating Yourself and Others
Education is a powerful tool in combating discrimination and fostering understanding. Learning about transfeminine identities, their challenges, and how to be a supportive ally can make a significant difference. Sharing this knowledge with others helps to spread awareness and promote acceptance.
Resources for Learning
A wealth of resources is available for those wishing to educate themselves about transfeminine identities. Books, documentaries, podcasts, and online courses provide valuable insights into the experiences and challenges faced by the transfemme community. Engaging with these resources is the first step in becoming an informed and effective ally.
Encouraging Open Dialogue
Open dialogue is crucial for breaking down barriers and fostering understanding. Creating spaces for conversations about gender identity and transfeminine experiences allows for greater empathy and awareness. Encouraging respectful discussions in schools, workplaces, and community settings can lead to more inclusive environments.
Challenging Stereotypes and Biases
Challenging stereotypes and biases requires active engagement and reflection. Allies can help by questioning assumptions, confronting discriminatory behavior, and promoting inclusive language. This proactive approach contributes to creating a culture of acceptance and respect for transfeminine individuals.
Advocating for Inclusive Policies
Advocacy for inclusive policies is essential in creating systemic change. Supporting organizations that work towards legal recognition and protection for transfeminine individuals can help to address some of the structural barriers they face.
Supporting Policy Change
Policy change is often driven by collective advocacy efforts. Allies can support policy change by engaging with advocacy organizations, participating in campaigns, and contacting legislators. These actions contribute to creating legal frameworks that protect and empower transfeminine individuals.
Promoting Workplace Inclusivity
Workplace inclusivity is a critical area for policy advocacy. Implementing policies that protect against discrimination and promote diversity can create safer and more equitable work environments. Allies can advocate for these changes within their own organizations and industries.
Engaging in Community Activism
Community activism is a powerful way to support the transfemme community. Participating in local events, supporting grassroots organizations, and raising awareness through social media are effective ways to contribute to the movement for equality and justice.
Creating Safe Spaces
Safe spaces are critical for the well-being of transfeminine individuals. Whether it’s in workplaces, schools, or social settings, creating environments where people can express themselves freely without fear of discrimination is vital.
Building Inclusive Schools
Schools play a crucial role in shaping young people’s understanding of gender and identity. Implementing inclusive curricula, supporting gender-neutral facilities, and training staff on gender sensitivity can create safer educational environments for transfeminine students.
Fostering Acceptance in Social Spaces
Social spaces, such as clubs, community centers, and recreational areas, should be welcoming for all individuals, regardless of gender identity. Establishing clear anti-discrimination policies and promoting awareness can help foster acceptance and inclusivity in these settings.
Cultivating Supportive Work Environments
Workplaces that prioritize inclusivity and support for transfeminine employees benefit from diverse perspectives and talents. Allies can advocate for policies and practices that ensure equal opportunities and create a culture of respect and acceptance.
Providing Emotional Support
Being a source of emotional support for transfeminine individuals can have a profound impact. Listening, offering empathy, and validating their experiences are simple yet powerful ways to show support.
Practicing Active Listening
Active listening involves giving full attention and understanding to the speaker, without judgment or interruption. Practicing active listening with transfeminine individuals shows respect for their experiences and provides a supportive space for them to share their stories.
Offering Empathy and Understanding
Empathy involves recognizing and validating the feelings and experiences of others. Offering empathy to transfeminine individuals can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a sense of connection and support. Allies can demonstrate empathy by acknowledging the challenges and celebrating the successes of transfemme individuals.
Encouraging Self-Care and Well-Being
Self-care is vital for the mental and emotional well-being of transfeminine individuals. Encouraging practices that promote self-care, such as mindfulness, exercise, and creative expression, can help build resilience and improve overall quality of life.
Conclusion
Navigating life as a transfemme individual involves embracing one’s identity while overcoming various societal and personal challenges. Through understanding, advocacy, and support, we can contribute to a more inclusive world where transfeminine people can thrive. Recognizing the significance of identities like transfeminine, and the symbols like the transfeminine flag, is a step towards greater acceptance and equality for all.
In fostering a community that values diversity and inclusion, we honor the experiences and identities of transfeminine individuals and work towards a future where everyone can live authentically and with dignity. By taking actionable steps to educate ourselves, advocate for change, and provide support, we can help create a society that celebrates and uplifts all individuals, regardless of their gender identity.
Q&A
Question: What does “transfeminine” mean, and how can identity and expression vary? Short answer: “Transfeminine” describes people assigned male at birth who identify more closely with femininity than masculinity. It sits under the broader transgender umbrella and includes diverse identities: some identify as women, others as non-binary or gender-fluid. Gender expression—through clothing, makeup, behavior, or other traits—can be fluid and change over time, underscoring that gender exists on a spectrum rather than a strict binary.
Question: Do transfeminine people need to medically transition to be valid? Short answer: No. Medical transition is a personal choice. Some transfeminine individuals pursue hormone therapy or gender-affirming surgeries; others do not—by preference or due to barriers like cost and access. There is no single “right” way to be transfeminine, and respecting each person’s decisions and timeline is essential.
Question: What does the transfeminine flag represent, and why does it matter? Short answer: The transfeminine flag uses soft pink and blue, often with white, to symbolize femininity, acknowledgment of masculine aspects some may relate to, and inclusion of non-binary or gender non-conforming people. It evolved from variations of the transgender flag to offer a distinct symbol for the community. Beyond pride and visibility, the flag is a tool for advocacy—sparking conversation, raising awareness, and reminding the public of ongoing struggles for rights and recognition.
Question: What are the key challenges transfemme individuals commonly face? Short answer: Challenges span social, institutional, and personal dimensions, including:
- Discrimination and misunderstandings that affect healthcare, employment, and housing access
- Misrepresentation or invisibility in media, which fuels stereotypes
- Safety concerns in public spaces (e.g., bathrooms, transit, social venues)
- Workplace bias and hostile environments
- Healthcare barriers, such as limited provider competence and hurdles to gender-affirming care
- Mental health needs intensified by stigma and rejection
- Uneven legal recognition, complicating IDs, protections, and access to services
Question: How can allies effectively support transfemme people? Short answer: Allies can pair learning with action:
- Educate yourself and share accurate information; encourage open, respectful dialogue
- Challenge stereotypes, bias, and discriminatory behavior; use inclusive language
- Advocate for inclusive policies and legal recognition; support anti-discrimination efforts
- Promote workplace inclusivity through protective policies and training
- Help create safe, welcoming spaces in schools, workplaces, and community settings
- Offer empathetic, judgment-free emotional support; practice active listening
- Encourage self-care and well-being, and connect people with supportive communities and resources